
三、Tornado进阶
3.1 Application
settings
debug,设置tornado是否工作在调试模式,默认为False即工作在生产模式。当设置debug=True 后,tornado会工作在调试/开发模式,在此种模式下,tornado为方便我们开发而提供了几种特性:
自动重启,tornado应用会监控我们的源代码文件,当有改动保存后便会重启程序,这可以减少我们手动重启程序的次数。需要注意的是,一旦我们保存的更改有错误,自动重启会导致程序报错而退出,从而需要我们保存修正错误后手动启动程序。这一特性也可单独通过autoreload=True设置;
取消缓存编译的模板,可以单独通过compiled_template_cache=False来设置;
取消缓存静态文件hash值,可以单独通过static_hash_cache=False来设置;
提供追踪信息,当RequestHandler或者其子类抛出一个异常而未被捕获后,会生成一个包含追踪信息的页面,可以单独通过serve_traceback=True来设置。
使用debug参数的方法:
import tornado.web app = tornado.web.Application([], debug=True)
路由映射
先前我们在构建路由映射列表的时候,使用的是二元元组,如:
[(r'/index', IndexHandle)]
对于这个映射列表中的路由,实际上还可以传入多个信息,如:
[ (r"/index", IndexHandle), url(r"/test", TestHandle, {"subject":"python"}, name="python_url") ]
对于路由中的字典,会传入到对应的RequestHandler的initialize()方法中:
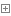
from tornado.web import RequestHandler class TestHandler(RequestHandler): def initialize(self, subject): self.subject = subject def get(self): self.write(self.subject)View Code
对于路由中的name字段,注意此时不能再使用元组,而应使用tornado.web.url来构建。name是给该路由起一个名字,可以通过调用RequestHandler.reverse_url(name)来获取该名子对应的url。

import tornado.web import tornado.httpserver import tornado.ioloop import tornado.options from tornado.options import options, define from tornado.web import url, RequestHandler define("port", default=8000, type=int, help="run server on the given port.") class IndexHandle(RequestHandler): """主路由处理类""" def get(self): python_url = self.reverse_url("python_url") self.write('<a href="/links.html?l=ZTNwWTlFblA5V05Jc0pXRmI3bDVtUT09">index</a>' % python_url) class TestHandle(RequestHandler): """主路由处理类""" def initialize(self, subject): self.subject = subject def get(self): """对应http的get请求""" self.write(self.subject) if __name__ == '__main__': tornado.options.parse_command_line() # 输出多值选项 # print(tornado.options.options.test) app = tornado.web.Application([ (r"/index", IndexHandle), url(r"/python", TestHandle, {"subject":"python"}, name="python_url") ], debug=True ) http_server = tornado.httpserver.HTTPServer(app) http_server.listen(tornado.options.options.port) tornado.ioloop.IOLoop.current().start()View Code
3.2 输入
1. 获取查询字符串参数
get_query_argument(name, default=_ARG_DEFAULT, strip=True)
从请求的查询字符串中返回指定参数name的值,如果出现多个同名参数,则返回最后一个的值。
default为设值未传name参数时返回的默认值,如若default也未设置,则会抛出tornado.web.MissingArgumentError异常。
strip表示是否过滤掉左右两边的空白字符,默认为过滤。
get_query_arguments(name, strip=True)
从请求的查询字符串中返回指定参数name的值,注意返回的是list列表(即使对应name参数只有一个值)。若未找到name参数,则返回空列表[]。
strip同前。
从请求体中返回指定参数name的值,如果出现多个同名参数,则返回最后一个的值。
default与strip同前。
get_body_arguments(name, strip=True)
从请求体中返回指定参数name的值,注意返回的是list列表(即使对应name参数只有一个值)。若未找到name参数,则返回空列表[]。
strip同前,不再赘述。
说明
对于请求体中的数据要求为字符串,且格式为表单编码格式(与url中的请求字符串格式相同),即key1=value1&key2=value2,HTTP报文头Header中的"Content-Type"为application/x-www-form-urlencoded 或 multipart/form-data。对于请求体数据为json或xml的,无法通过这两个方法获取。
3. 前两类方法的整合
get_argument(name, default=_ARG_DEFAULT, strip=True)
从请求体和查询字符串中返回指定参数name的值,如果出现多个同名参数,则返回最后一个的值。
default与strip同前。
get_arguments(name, strip=True)
从请求体和查询字符串中返回指定参数name的值,注意返回的是list列表(即使对应name参数只有一个值)。若未找到name参数,则返回空列表[]。
strip同前。
说明
对于请求体中数据的要求同前。 这两个方法最常用。
用代码来看上述六中方法的使用:

import tornado.web import tornado.httpserver import tornado.ioloop import tornado.options from tornado.options import options, define from tornado.web import url, RequestHandler define("port", default=8000, type=int, help="run server on the given port.") class IndexHandle(RequestHandler): """主路由处理类""" def post(self): query_arg = self.get_query_argument("a") query_args = self.get_query_arguments("a") body_arg = self.get_body_argument("a") body_args = self.get_body_arguments("a", strip=False) arg = self.get_argument("a") args = self.get_arguments("a") # self.write(query_arg) self.write(str(query_args)) if __name__ == '__main__': tornado.options.parse_command_line() # 输出多值选项 # print(tornado.options.options.test) app = tornado.web.Application([ (r"/index", IndexHandle) ], debug=True ) http_server = tornado.httpserver.HTTPServer(app) http_server.listen(tornado.options.options.port) tornado.ioloop.IOLoop.current().start()View Code
4. 关于请求的其他信息
RequestHandler.request 对象存储了关于请求的相关信息,具体属性有:
method HTTP的请求方式,如GET或POST;
host 被请求的主机名;
uri 请求的完整资源标示,包括路径和查询字符串;
path 请求的路径部分;
query 请求的查询字符串部分;
version 使用的HTTP版本;
headers 请求的协议头,是类字典型的对象,支持关键字索引的方式获取特定协议头信息,例如:request.headers["Content-Type"]
body 请求体数据; (获取json数据:request.body)
remote_ip 客户端的IP地址;
files 用户上传的文件,为字典类型,型如:
{ "form_filename1":[<tornado.httputil.HTTPFile>, <tornado.httputil.HTTPFile>], "form_filename2":[<tornado.httputil.HTTPFile>,], ... }
tornado.httputil.HTTPFile是接收到的文件对象,它有三个属性:
filename 文件的实际名字,与form_filename1不同,字典中的键名代表的是表单对应项的名字;
body 文件的数据实体;
content_type 文件的类型。
这三个对象属性可以像字典一样支持关键字索引,如request.files["form_filename1"][0]["body"]。
上传文件并保存在服务器本地的小程序upload.py:

import tornado.web import tornado.ioloop import tornado.httpserver import tornado.options from tornado.options import options, define from tornado.web import RequestHandler define("port", default=8000, type=int, help="run server on the given port.") class IndexHandler(RequestHandler): def get(self): self.write("hello tornado.") class UploadHandler(RequestHandler): def post(self): files = self.request.files img_files = files.get('img') if img_files: img_file = img_files[0]["body"] file = open("./test", 'w+') file.write(img_file) file.close() self.write("OK") if __name__ == "__main__": tornado.options.parse_command_line() app = tornado.web.Application([ (r"/", IndexHandler), (r"/upload", UploadHandler), ]) http_server = tornado.httpserver.HTTPServer(app) http_server.listen(options.port) tornado.ioloop.IOLoop.current().start()View Code
5. 正则提取uri
tornado中对于路由映射也支持正则提取uri,提取出来的参数会作为RequestHandler中对应请求方式的成员方法参数。若在正则表达式中定义了名字,则参数按名传递;若未定义名字,则参数按顺序传递。提取出来的参数会作为对应请求方式的成员方法的参数。

import tornado.web import tornado.ioloop import tornado.httpserver import tornado.options from tornado.options import options, define from tornado.web import RequestHandler define("port", default=8000, type=int, help="run server on the given port.") class IndexHandler(RequestHandler): def get(self): self.write("hello tornado.") class SubjectCityHandler(RequestHandler): def get(self, subject, city): self.write(("Subject: %s<br/>City: %s" % (subject, city))) class SubjectDateHandler(RequestHandler): def get(self, date, subject): self.write(("Date: %s<br/>Subject: %s" % (date, subject))) if __name__ == "__main__": tornado.options.parse_command_line() app = tornado.web.Application([ (r"/", IndexHandler), (r"/sub-city/(.+)/([a-z]+)", SubjectCityHandler), # 无名方式 (r"/sub-date/(?P<subject>.+)/(?P<date>d+)", SubjectDateHandler), # 命名方式 ]) http_server = tornado.httpserver.HTTPServer(app) http_server.listen(options.port) tornado.ioloop.IOLoop.current().start()View Code

3.3 输出
1. write(chunk)
将chunk数据写到输出缓冲区。如我们在之前的示例代码中写的:

class IndexHandle(RequestHandler): """主路由处理类""" def get(self): self.write("test1")View Code
在同一个处理方法中多次使用write方法

class IndexHandle(RequestHandler): def get(self): self.write("test1") self.write("test2") self.write("test3")View Code
write方法是写到缓冲区的,我们可以像写文件一样多次使用write方法不断追加响应内容,最终所有写到缓冲区的内容一起作为本次请求的响应输出。

利用write方法写json数据

class IndexHandle(RequestHandler): """主路由处理类""" def get(self): data = { "name":"zhangsan", "age":24, "gender":1, } data_str = json.dumps(data) self.write(data_str)View Code
实际上,我们可以不用自己手动去做json序列化,当write方法检测到我们传入的chunk参数是字典类型后,会自动帮我们转换为json字符串。

class IndexHandle(RequestHandler): def get(self): data = { "name":"zhangsan", "age":24, "gender":1, } # data_str = json.dumps(data) self.write(data)View Code
两种方式有什么差异?
对比一下两种方式的响应头header中Content-Type字段,自己手动序列化时为Content-Type:text/html; charset=UTF-8,而采用write方法时为Content-Type:application/json; charset=UTF-8。
write方法除了帮我们将字典转换为json字符串之外,还帮我们将Content-Type设置为application/json; charset=UTF-8。
2. set_header(name, value)
利用set_header(name, value)方法,可以手动设置一个名为name、值为value的响应头header字段。
用set_header方法来完成上面write所做的工作。

class IndexHandle(RequestHandler): def get(self): data = { "name":"zhangsan", "age":24, "gender":1, } data_str = json.dumps(data) self.write(data) self.set_header("Content-Type", "application/json; charset=UTF-8")View Code
3. set_default_headers()
该方法会在进入HTTP处理方法前先被调用,可以重写此方法来预先设置默认的headers。注意:在HTTP处理方法中使用set_header()方法会覆盖掉在set_default_headers()方法中设置的同名header。

import tornado.web import tornado.httpserver import tornado.ioloop import tornado.options from tornado.options import options, define from tornado.web import url, RequestHandler import json define("port", default=8000, type=int, help="run server on the given port.") class IndexHandle(RequestHandler): def set_default_headers(self): print("执行了set_default_headers()") # 设置get与post方式的默认响应体格式为json self.set_header("Content-Type", "application/json; charset=UTF-8") # 设置一个名为itcast、值为python的header self.set_header("book", "python") def get(self): data = { "name":"zhangsan", "age":24, "gender":1, } data_str = json.dumps(data) self.write(data) self.set_header("name", "test") def
 登录查看全部
登录查看全部
参与评论
手机查看
返回顶部